版本:vue@2.2.3 文件路径:vue/dist/vue.runtime.esm.js(运行时构建、ES Module版本)
何为 Vue2.0
Vue.js —— The Progressive JavaScript Framework
它是一个渐进式 JavaScript 框架
与其他重量级框架不同的是,Vue 采用自底向上增量开发的设计。 Vue 的核心库只关注视图层,并且非常容易学习,非常容易与其它库或已有项目整合。 另一方面,Vue 完全有能力驱动采用单文件组件和 Vue 生态系统支持的库开发的复杂单页应用。
Vue.js 的目标是通过尽可能简单的 API 实现响应的数据绑定和组合的视图组件
如何上手
简而言之,即命令行以下五步
# 全局安装 vue-cli
$ npm install --global vue-cli
# 创建一个基于 webpack 模板的新项目
$ vue init webpack my-project
$ cd my-project
# 安装依赖,走你
$ npm install
$ npm run dev
像样的vue2.0目录结构
webpack
|---build webpack build 的 各个配置文件
|---config 不同环境的基础配置
|---dist npm run build 生成的output文件
|---node_modules 引用的npm生态圈的模块
|---src 项目的根目录
|---api 放置各个服务端接口
|---index.js index接口
|---components 模块内部的组件 也就是页面级的组件
|---header header组件
|---header.vue
|---imgs
|--head.jpg
|---store vuex的store数据模块 各模块划分请参考vuex使用文档
|---actions.js
|---getters.js
|---index.js
|---mutation-types.js
|---mutation.js
|---state.js
|---App.vue 模块的主vue 包含模板 逻辑 样式
|---main.html 模块的入口html
|---main.js 模块的入口js
|---static 图片等静态资源
|---.babelrc babel语法的配置文件
|---.editorconfig 编辑器的配置文件 -> 规范接入的同学
|---.eslintignore 配置eslint语法检测忽略的文件
|---.eslintrc.js eslint语法检测的配置文件
|---.gitignore git提交忽略的文件
|---package.json 依赖包配置
你可能好奇通过 vue-cli 生成的目录
和上面👆有点区别,
是的,上面目录中添加了store目录状态维护池bus,
同时,将api请求从业务代码分离出来 目录结构更清晰
这里涉及两个知识点 vuex 和 vue-resource
项目的入口
在 /src/main.js 中的
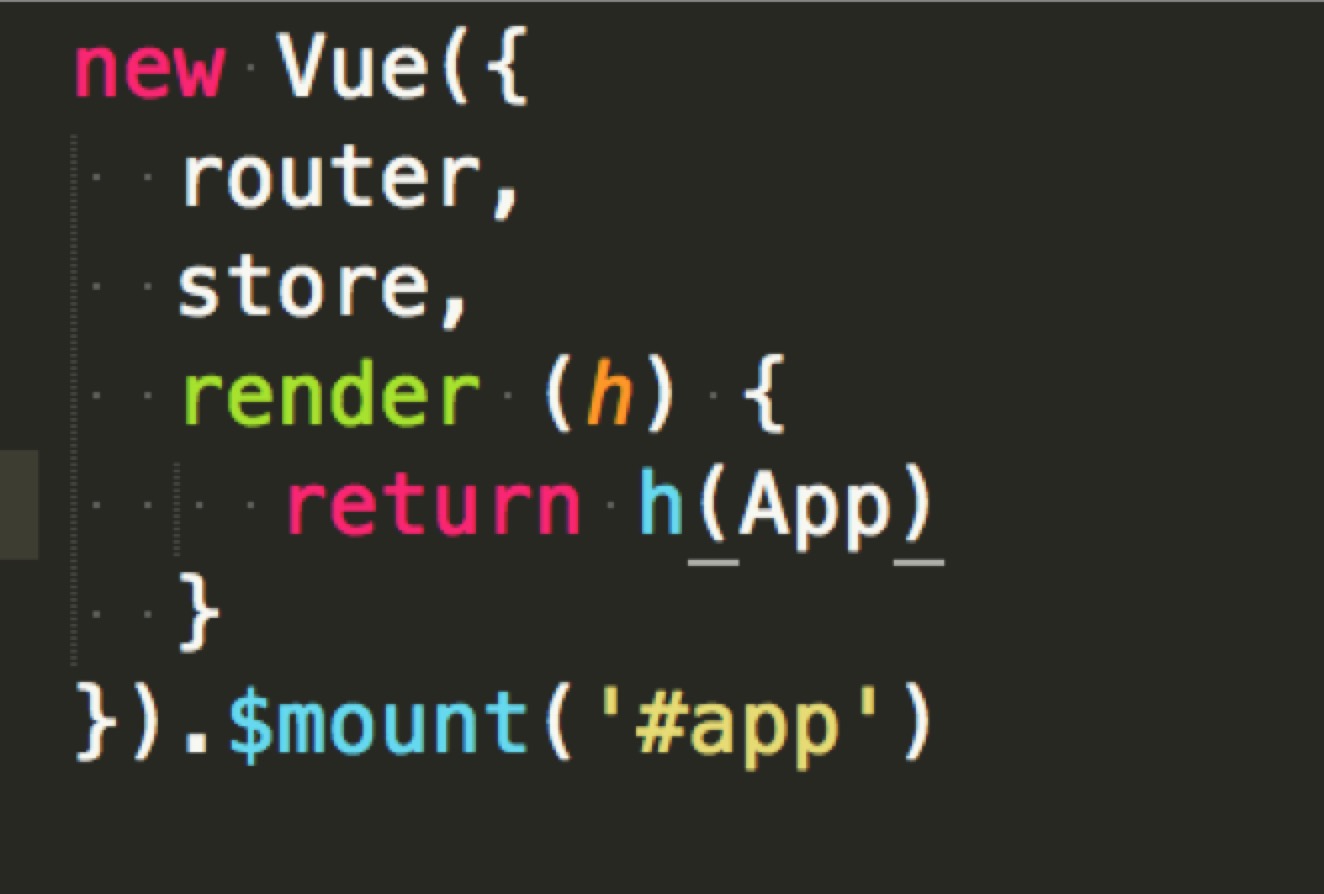
这里,new 实例化 vue 对象,同时传入配置项 router、store、render
并且挂载到 id = 'app' 的 DOM 节点上
注意:render 函数返回的是 h(App) ,App 就是 import 的App.vue组件
一般习惯 h 指 createElement 函数的简写
知识点 好奇这段代码的写法,你就该好好看看 es6语法 了~
进军源码世界
生命周期
分析 vue2.0 的源码,首先从它的生命周期图开始说起
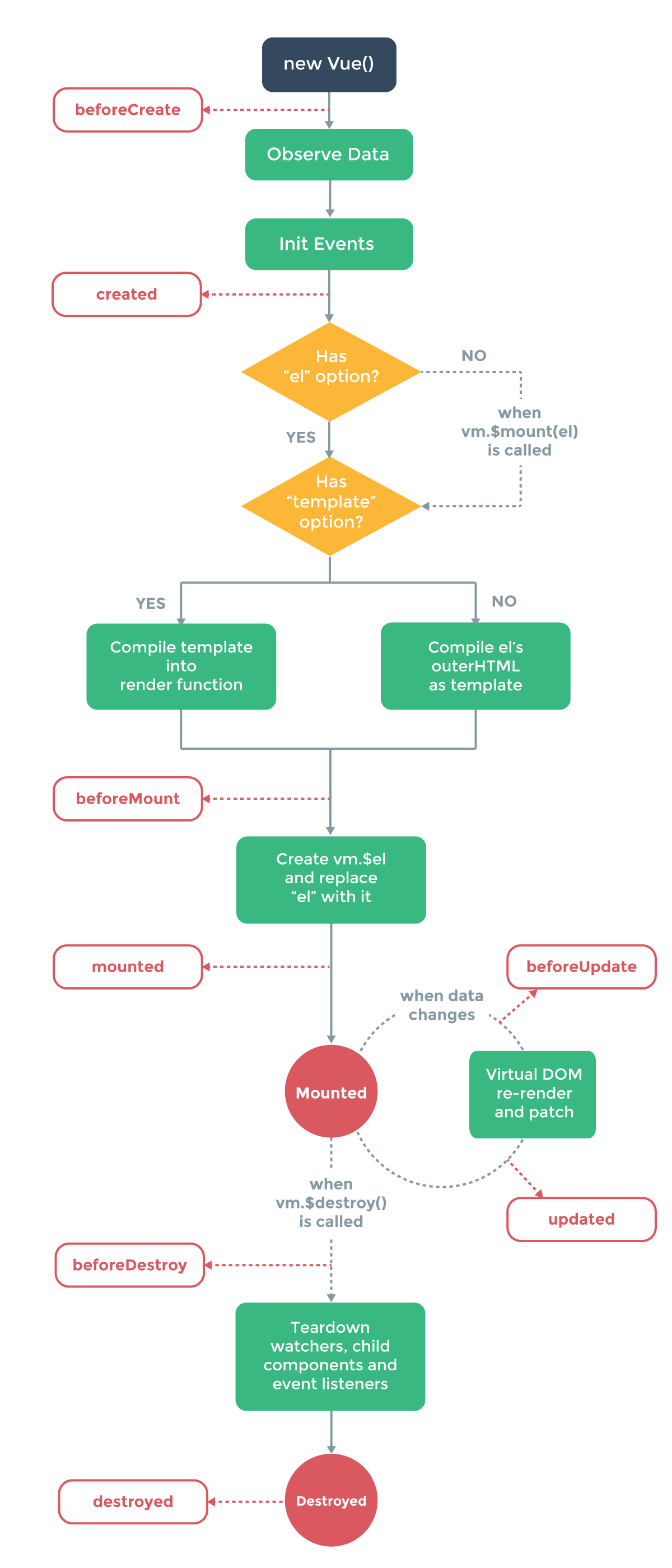
生命周期主要分为4个过程:
create: new Vue时,会先进行create,创建出Vue对象。mount: 根据el, template, render方法等属性,会生成DOM,并添加到对应位置。update: 当数据发生变化后,会重新渲染DOM,并进行替换。destory: 销毁时运行。
接下来的源码解读,也是按上面4个过程循序渐进
入口文件在哪?
在 /node_moudles/vue/src/core/instance/ 目录下
Vue 原型对象及其方法的声明,分散在此目录的多个文件中:
init.js:._init()state.js:.$data .$set() .$delete() .$watch()render.js:._render() …events.js:.$on() .$once() .$off() .$emit()lifecycle.js:._mount() ._update() .$forceUpdate() .$destroy()
create: Vue 原型对象的声明
1.声明 Vue 构造函数,调用 _init 方法,传入 options
注:// … 代表省略的上下文代码
// src/core/instance/index.js
// 1-1 Vue 定义
function Vue (options) {
// ...
// 1-2 ./init.js
this._init(options)
}
// 1-3 ./init.js
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
// 执行后 定义与生命周期相关的原型方法
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
// 1-4 执行renderMixin 在./render.js中定义 定义了vm._render()渲染VNode方法
// 执行后 定义与渲染相关的原型方法
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue
2._init 方法,初始化多个过程,包括初始化 initLifecycle(生命周期)、initEvents(事件监听)、initRender(渲染)、initInjections
initState(状态)、initProvide;最后执行 vm.$mount(vm.$options.el) 挂载 el
知识点
好奇
_init方法的传参,你就该好好看看 静态类型检查工具 flow 了~
简言之,
options?: Object指明 传参options变量类型必须是 对象
// src/core/instance/init.js
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
// ...
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
// 1-2-4 调用initRender 渲染VNode src/core/instance/render.js
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm) // 1-2-5 在initState中,会对Props, Data, Computed等属性添加Setter/Getter 在src/core/instance/state.js
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false)
mark('init end')
measure(`${vm._name} init`, 'init', 'init end')
}
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
mount: Vue 挂载 el
👇关键点:
vue 有两种构建方式:独立构建和运行构建,区别在于前者包含模板编译器而后者不包含
详细介绍见 vue中文文档
注:模板编译用于编译 Vue 模板字符串成纯 JavaScript 渲染函数
简言之,
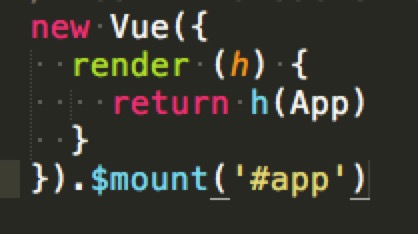
// 在入口 `main.js` 中
// 运行构建只能通过 `render` 选项,加载模板
new Vue({
render (h) {
return h(App)
}
}).$mount('#app')
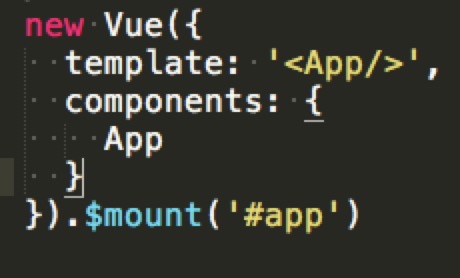
// 而不支持下面👇的 `template` 选项
new Vue({
template: '<App/>',
components: {
App
}
}).$mount('#app')
但即使使用运行时构建,在单文件组件中也依然可以写模板。
独立构建(vue/dist/vue.esm.js)打包了 src/entries/web-runtime-with-compiler.js 和 src/entries/web-runtime.js
运行构建(vue/dist/vue.runtime.esm.js) 只打包了 src/entries/web-runtime.js
下面👇对 Vue.prototype.$mount 的分析基于运行时构建(vue/dist/vue.runtime.esm.js)的源码,也就是在src/entries/web-runtime.js定义
默认 NPM 包导出的是运行时构建。运行时构建比独立构建要轻量30%,只有 17.14 Kb min+gzip大小
注:这里有 vue/dist 目录下各文件说明 https://github.com/vuejs/vue/blob/dev/dist/README.md
| 打包规范 | UMD | CommonJS | ES Module |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full(Runtime + Compiler) | vue.js | vue.common.js | vue.esm.js |
| Runtime-only | vue.runtime.js | vue.runtime.common.js | vue.runtime.esm.js |
| Full (production) | vue.min.js | ||
| Runtime-only (production) | vue.runtime.min.js |
src/entries/web-runtime.js中的Vue.prototype.$mount方法定义
// src/entries/web-runtime.js
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
// ...
// 1-2-3-6-2 core/instance/lifecycle.js
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}
调用 mountComponent 方法,这里的 vm.$options.render 是重点,打个断点 debugger
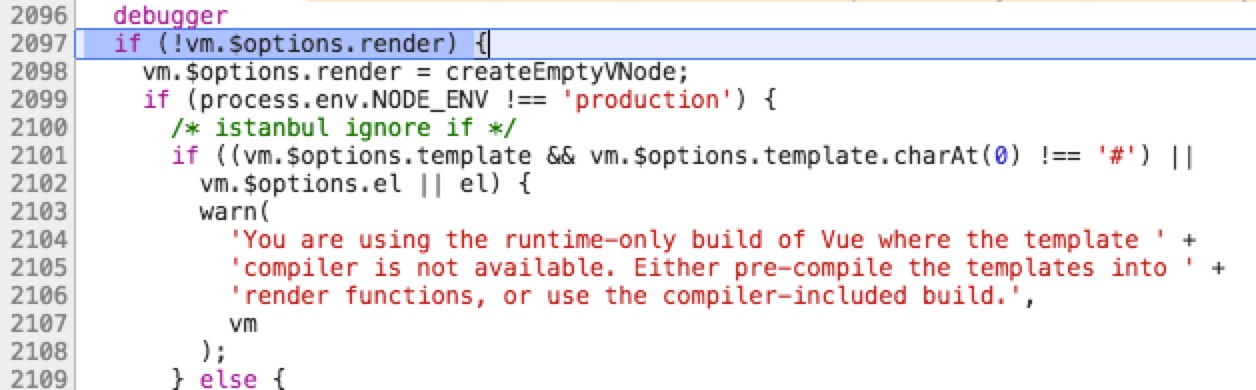
下表可见不同引用方式,渲染方法 render 不同
| 引用方式 | vm.$options.render | 详细说明 |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
render 选项,只能使用运行时构建(vue/dist/vue.runtime.esm.js) |
 |
 |
支持template 的选项 属于 包含模板编译器的 独立构建(vue/dist/vue.esm.js),其 render 方法的具体实现 参照扩展阅读 |
单组件文件(各种.vue组件) |
 |
单文件组件的模板会在构建时预编译为 render 函数 |
可见,vm.$options.render 方法与调用方式有关
// src/core/instance/lifecycle.js
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
vm.$el = el
if (!vm.$options.render) {
vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode;
// ...
}
// 1-2-3-6-2-2 触发 beforeMount 事件
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
let updateComponent
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
updateComponent = () => {
// ...
vm._update(vnode, hydrating)
}
} else {
// _render 在 ./render.js中定义
updateComponent = () => {
// 1-2-3-6-2-5
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
}
// new一个watcher对象 会运行传入的方法vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
vm._watcher = new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop)
hydrating = false
// manually mounted instance, call mounted on self
// mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
return vm
}
上面👆有两个地方需要关注
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)更新视图操作new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop)这是实现数据双向绑定的关键
接下来,先介绍 vm._render 方法的声明和定义。
render: 渲染
vm._render 返回虚拟DOM
// src/core/instance/render.js
// 1-2-3-6-2-3-1 1-4-3 : VNode限定返回值为VNode对象
Vue.prototype._render = function (): VNode {
const vm: Component = this
const {
render,
staticRenderFns,
_parentVnode
} = vm.$options
// ...
vm.$vnode = _parentVnode
// render self
let vnode
try {
vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, vm, `render function`)
// ...
}
// ...
// set parent
vnode.parent = _parentVnode
// 1-2-3-6-2-3-2 1-4-4
return vnode
}
由上面表格的第一种引用方式配置 render 选项可知,
这里 vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement) 等价于
执行 vnode = vm.$createElement(App)
接下来看看 createElement 的实现
// src/core/vdom/create-element.js
export function createElement (
context: Component,
tag: any,
data: any,
children: any,
normalizationType: any,
alwaysNormalize: boolean
): VNode {
if (Array.isArray(data) || isPrimitive(data)) {
normalizationType = children
children = data
data = undefined
}
if (alwaysNormalize) normalizationType = ALWAYS_NORMALIZE
return _createElement(context, tag, data, children, normalizationType)
}
export function _createElement (
context: Component,
tag?: string | Class<Component> | Function | Object,
data?: VNodeData,
children?: any,
normalizationType?: number
): VNode {
if (data && data.__ob__) {
return createEmptyVNode()
}
if (!tag) {
// in case of component :is set to falsy value
return createEmptyVNode()
}
// support single function children as default scoped slot
if (Array.isArray(children) &&
typeof children[0] === 'function') {
data = data || {}
data.scopedSlots = { default: children[0] }
children.length = 0
}
if (normalizationType === ALWAYS_NORMALIZE) {
children = normalizeChildren(children)
} else if (normalizationType === SIMPLE_NORMALIZE) {
children = simpleNormalizeChildren(children)
}
let vnode, ns
if (typeof tag === 'string') {
let Ctor
ns = config.getTagNamespace(tag)
if (config.isReservedTag(tag)) {
// platform built-in elements
vnode = new VNode(
config.parsePlatformTagName(tag), data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
} else if ((Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag))) {
// component
vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag)
} else {
// unknown or unlisted namespaced elements
// check at runtime because it may get assigned a namespace when its
// parent normalizes children
vnode = new VNode(
tag, data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
}
} else {
// direct component options / constructor
vnode = createComponent(tag, data, context, children)
}
if (vnode) {
if (ns) applyNS(vnode, ns)
return vnode
} else {
return createEmptyVNode()
}
}
以上👆是 VNode 的生成方式,有兴趣可阅读 createComponent 方法的实现,此处不展开
update: 更新视图
回到mount挂载时的关注点,vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
以vm._render()生成的虚拟DOM为参,更新视图
// src/core/instance/lifecycle.js
// 1-2-3-6-2-6 vm._update原型方法 通过vm._render()拿到vNode后,进行DOM更新。
Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode: VNode, hydrating?: boolean) {
const vm: Component = this
if (vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
const prevEl = vm.$el
const prevVnode = vm._vnode
const prevActiveInstance = activeInstance
activeInstance = vm
vm._vnode = vnode
// Vue.prototype.__patch__ is injected in entry points
// based on the rendering backend used.
// 1-2-3-6-2-7
if (!prevVnode) {
// initial render 1-2-3-6-2-8 首次添加
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(
vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false /* removeOnly */,
vm.$options._parentElm,
vm.$options._refElm
)
} else {
// updates
// 1-2-3-6-2-9 在 src/core/vdom/patch.js 定义
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode) // 数据变化后触发的DOM更新
}
activeInstance = prevActiveInstance
// update __vue__ reference
if (prevEl) {
prevEl.__vue__ = null
}
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = vm
}
// if parent is an HOC, update its $el as well
if (vm.$vnode && vm.$parent && vm.$vnode === vm.$parent._vnode) {
vm.$parent.$el = vm.$el
}
// updated hook is called by the scheduler to ensure that children are
// updated in a parent's updated hook.
}
这里涉及到 VNode 和 DOM 节点的绑定__patch__,实现数据变化后触发的DOM更新
接下来,看看 vm.__patch__ 的源码实现
// src/core/vdom/patch.js
export function createPatchFunction (backend) {
// ...
// patch通过patchVnode来更新根节点
function patchVnode (oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
// ...
if (isUndef(vnode.text)) {
if (isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch)) {
// 1-2-3-6-2-9-2-2 通过updateChildren来更新子节点
if (oldCh !== ch) updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly)
} else if (isDef(ch)) {
if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else if (isDef(oldCh)) {
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1)
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text)
}
if (hasData) {
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.postpatch)) i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
}
// ...
return function patch (oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly, parentElm, refElm) {
if (!vnode) {
if (oldVnode) invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
return
}
let isInitialPatch = false
const insertedVnodeQueue = []
if (!oldVnode) {
// empty mount (likely as component), create new root element
isInitialPatch = true
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm)
} else {
const isRealElement = isDef(oldVnode.nodeType)
if (!isRealElement && sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
// patch existing root node
// 1-2-3-6-2-9-2
// diff并更新DOM。
// 如果是update,则会调动patchVnode()
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly)
} else {
// ...
}
}
// 1-2-3-6-2-9-3 element insert到DOM中
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, isInitialPatch)
return vnode.elm
}
}
小结一下
new Vue的过程主要涉及到三个对象:
vm、compiler、watcher
其中,
vm表示Vue的具体对象;compiler负责将template解析为AST render方法;watcher用于观察数据变化,以实现数据变化后进行re-render。
如下图所示,
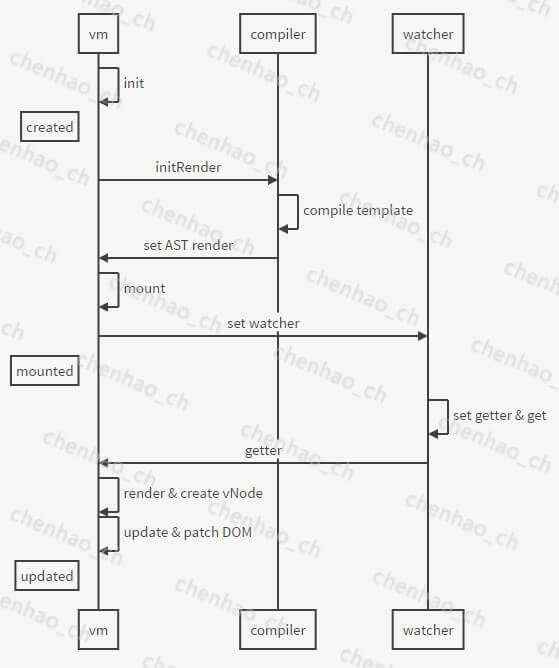
从template到DOM,有三个过程:
- template -> AST render(compiler解析template)
- AST render -> vNode (render方法运行)
- vNode -> DOM (vdom.patch)
Watcher —— 实现双向数据绑定
整个Watcher的过程可以分为三个过程:
- 对
state设置setter/getter - 对
vm设置好Watcher,添加好state触发setter时的执行方法 state变化触发执行
下面👇以 data 数据举例说明 Vue 2.0 如何实现双向数据绑定
回到文件 src/core/instance/init.js Vue.prototype._init 方法里的 initState(vm)
Vue 2.0 在 init 的过程中,执行 initState(vm) 初始化状态,会对Props, Data, Computed等属性添加 Setter/Getter
// src/core/instance/state.js
export function initState (vm: Component) {
vm._watchers = []
const opts = vm.$options
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)
if (opts.data) {
// 1-2-5-2 以 initData 举例说明 双向数据绑定
initData(vm)
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)
}
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)
if (opts.watch) initWatch(vm, opts.watch)
}
// ...
// 1-2-5-2-1 初始化 data
function initData (vm: Component) {
let data = vm.$options.data
data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function'
? data.call(vm)
: data || {}
// ...
// proxy data on instance
const keys = Object.keys(data)
const props = vm.$options.props
let i = keys.length
while (i--) {
if (props && hasOwn(props, keys[i])) {
// ...
} else if (!isReserved(keys[i])) {
proxy(vm, `_data`, keys[i]) // 1-2-5-2-2 设置vm._data为代理
}
}
// observe data
// 1-2-5-2-3 通过调用observe方法,会对data添加好观察者
// 在 src/core/observer/index.js 定义
observe(data, true /* asRootData */)
}
看到 observe(data, true /* asRootData */),对 data 进行监听
// src/core/observer/index.js
export function observe (value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void {
if (!isObject(value)) {
return
}
let ob: Observer | void
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__
} else if (
observerState.shouldConvert &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
// 1-2-5-2-3-2 没有则新建 observer 实例
ob = new Observer(value)
}
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++
}
return ob
}
/**
* Observer构造函数
* Observer 会和被观察的对象绑定,
* 并且将目标对象的健 key 转换成 包含getter/setters属性,
* 就能够收集依赖 dep 同时分发 update
*/
export class Observer {
value: any;
dep: Dep;
vmCount: number; // number of vms that has this object as root $data
constructor (value: any) {
this.value = value
this.dep = new Dep()
this.vmCount = 0
def(value, '__ob__', this)
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
const augment = hasProto
? protoAugment
: copyAugment
augment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys)
// 1-2-5-2-3-2-2
// Array 则执行 observeArray to convert
this.observeArray(value)
} else {
// 1-2-5-2-3-2-3
// Array 则执行 walk to convert
this.walk(value)
}
}
/**
* Walk through each property and convert them into
* getter/setters. This method should only be called when
* value type is Object.
*/
walk (obj: Object) {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
// 1-2-5-2-3-2-3-2
defineReactive(obj, keys[i], obj[keys[i]])
}
}
// ...
}
// 1-2-5-2-3-2-3-2-1 给 Object 定义响应式属性
export function defineReactive (
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: Function
) {
const dep = new Dep()
// ...
let childOb = observe(val)
// 1-2-5-2-3-2-3-2-2 定义属性
// 可参考此方法给对象添加新属性
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend() // 1-2-5-2-3-2-3-2-3 处理好依赖watcher
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
}
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter()
}
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
childOb = observe(newVal) // 1-2-5-2-3-2-3-2-4 对新数据重新observe
dep.notify() // 1-2-5-2-3-2-3-2-5 通知到dep进行数据更新 在 src/core/observer/dep.js 定义
}
})
}
这里的重点是 defineProperty 方法,给对象添加新属性 getter/setter
看到 const dep = new Dep() 给 data 新建 Dep 依赖池,我们来看看 Dep 是什么东东
// src/core/observer/dep.js
/**
* A dep is an observable that can have multiple
* directives subscribing to it.
*/
/**
* 一个 dep 是可以被多个指令订阅
*/
// 1-2-5-2-3-2-3-2-5-1 dep 相当于媒介 将观察者 和 目标数据关联起来
export default class Dep {
static target: ?Watcher;
id: number;
subs: Array<Watcher>;
constructor () {
this.id = uid++
this.subs = []
}
// 1-2-5-2-3-2-3-2-5-2 将 观察者(订阅者)们 收集起来
addSub (sub: Watcher) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
removeSub (sub: Watcher) {
remove(this.subs, sub)
}
// 1-2-5-2-3-2-3-2-5-3 给 Dep 的 观察者们 关联 媒介实例
depend () {
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this)
}
}
// 1-2-5-2-3-2-3-2-5-4 更新 target watcher being evaluated
notify () {
// stabilize the subscriber list first
const subs = this.subs.slice()
for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
// 1-2-5-2-3-2-3-2-5-5 在 src/core/observer/watcher.js 中定义
subs[i].update()
}
}
}
可以看到,这里 subs 数组收集的是 watcher 实例,而 subs[i].update() 实际执行的是 Watcher 的原型方法 update
先往前面回忆,回到代码 src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 处的关注点
vm._watcher = new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop)
那 Watcher 的构造函数在哪呢?请看下面👇
其中,this.getter 属性 会获取传入的 updateComponent 值
// src/core/observer/watcher.js
export default class Watcher {
vm: Component;
expression: string;
cb: Function;
id: number;
deep: boolean;
user: boolean;
lazy: boolean;
sync: boolean;
dirty: boolean;
active: boolean;
deps: Array<Dep>;
newDeps: Array<Dep>;
depIds: Set;
newDepIds: Set;
getter: Function;
value: any;
constructor (
vm: Component,
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: Function,
options?: Object
) {
this.vm = vm
vm._watchers.push(this)
// ...
if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') {
// 在此赋值 回调到 src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 声明 new Watcher 的地方
this.getter = expOrFn
} else {
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn)
if (!this.getter) {
this.getter = function () {}
// ...
}
}
// Watcher会在构造完成后主动调用this.get()来触发this.getter()方法的运行,以达到更新DOM节点
this.value = this.lazy
? undefined
: this.get()
}
/**
* Evaluate the getter, and re-collect dependencies.
*/
get () {
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
if (this.user) {
try {
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
}
} else {
// 通过调用 this.getter 更新 DOM
// 在src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 声明 new Watcher 的地方 赋值了
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
}
// ...
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
return value
}
/**
* Add a dependency to this directive.
*/
addDep (dep: Dep) {
const id = dep.id
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
this.newDepIds.add(id)
this.newDeps.push(dep)
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this)
}
}
}
/**
* Clean up for dependency collection.
*/
cleanupDeps () {
// ...
}
/**
* Subscriber interface.
* Will be called when a dependency changes.
*/
// Watcher 的 update 方法
update () {
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
// 调用 run() 方法
this.run()
} else {
// 通过nextTicker来执行run方法
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
/**
* Scheduler job interface.
* Will be called by the scheduler.
*/
run () {
if (this.active) {
// 调用 get 方法 更新 DOM
const value = this.get()
if (
value !== this.value ||
// Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even
// when the value is the same, because the value may
// have mutated.
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// set new value
const oldValue = this.value
this.value = value
if (this.user) {
try {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, this.vm, `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
}
} else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
}
}
}
}
// ...
/**
* Depend on all deps collected by this watcher.
*/
depend () {
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].depend()
}
}
/**
* Remove self from all dependencies' subscriber list.
*/
teardown () {
if (this.active) {
// remove self from vm's watcher list
// this is a somewhat expensive operation so we skip it
// if the vm is being destroyed.
if (!this.vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
remove(this.vm._watchers, this)
}
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].removeSub(this)
}
this.active = false
}
}
}
执行 Watcher 的原型方法 update ,会调用
run() -> get() -> this.getter -> updateComponent -> vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating),最后更新 DOM
数据绑定关系图如下所示,
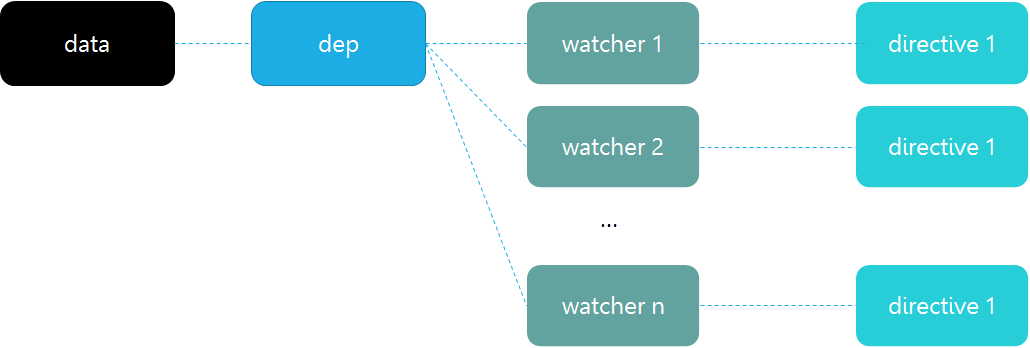
- 对数据读取时,如果当前有Watcher,那将该 Watcher 绑定到当前的数据上(dep.depend(),dep 关联当前数据和所有的 watcher 的依赖关系),是一个检查并记录依赖的过程。
- 而对数据赋值时,如果数据改变,则通知所有的 watcher(dep.notify())这样实现数据绑定
Watcher —— 总结
_init-> 对Data设置getter / setter:setter会调用dep.notify() ,以便数据变化时通知DOM进行更新。new Watcher时,配置更新DOM的方法 即Watcher.getter方法。- 当Data发生变化时,执行
dep.notify() -> watcher.getter()-> vm.render()、vm.update(),DOM更新
Vue2.0 基本运行机制总结为:
文本模板template,编译compile得到渲染函数(render),
该过程会识别并记录 Vue 的指令和其他语法,new Vue() 得到 vm 对象,
其中传入的数据会进行数据劫持处理,从而可以收集依赖,实现数据绑定
渲染过程是将所有数据交由渲染函数(render)进行调用,进而得到 vnode,应用 Virtual DOM 的机制实现初始渲染和更新
扩展阅读
独立构建 (vue/dist/vue.esm.js) 支线 即
src/entries/web-runtime-with-compiler.js中对Vue.prototype.$mount的继承定义
mount:挂载
在 entries/web-runtime-with-compiler.js 定义
// src/entries/web-runtime-with-compiler.js
// mount 临时存储Vue.prototype.$mount原值
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && query(el)
// ...
const options = this.$options
// 1-2-3-2
// resolve template/el and convert to render function
// 如果没有render方法
if (!options.render) {
let template = options.template
// ...
if (template) { // 1-2-3-5 如果获取到了模板,则将模板转化为render方法
// ...
// 1-2-3-7 compileToFunctions方法会运行compile将template解析为多个render方法,也就是AST render
// 定义在 src/platforms/web/compiler/index.js
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, {
shouldDecodeNewlines,
delimiters: options.delimiters
}, this)
options.render = render
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns
// ...
}
}
// 1-2-3-6 ./web-runtime.js
// 会调用./web-runtime.js 中的Vue.prototype.$mount方法
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)
}
如果有render方法,直接运行mount;
Vue 2.0中的模板有三种引用写法:el, template, render(JSX)。其中的优先级是 render > template > el
重点关注两个地方:
mount.call(this, el, hydrating)调用·./web-runtime.js文件 中的Vue.prototype.$mount方法compileToFunctions方法 生成的 AST render 方法
知识点:AST指 抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Tree)
render:渲染
// src/compiler/index.js
function compileToFunctions (
template: string,
options?: CompilerOptions,
vm?: Component
): CompiledFunctionResult {
options = options || {}
//...
// check cache
// 1-2-3-7-1-2 最终由compile方法 生成render
const compiled = compile(template, options)
//...
}
// 1-2-3-7-1-2-1 compile方法就是将template以AST的方式进行解析,并转化为render方法进行返回
function compile (
template: string,
options?: CompilerOptions
): CompiledResult {
// ...
// 1-2-3-7-1-2-2 核心
const compiled = baseCompile(template, finalOptions)
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
errors.push.apply(errors, detectErrors(compiled.ast))
}
compiled.errors = errors
compiled.tips = tips
return compiled
}
function baseCompile (
template: string,
options: CompilerOptions
): CompiledResult {
// 1-2-3-7-1-2-2-1 核心代码 attrsList 在 ./parser/index.js定义
const ast = parse(template.trim(), options) // 解析template为AST 抽象语法树 将最大静态子树提取出来
// 1-2-3-7-1-2-2-2 在 ./optimizer.js 中定义
optimize(ast, options) // 提取static tree
// 1-2-3-7-1-2-2-3
const code = generate(ast, options) // 生成render 方法
return {
ast,
render: code.render, // 1-2-3-7-1-2-2-4 编译得到 render 其实是代码文本,通过 new Function(code) 的方式转为函数
staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns
}
}
方法调用过程为: createCompiler -> compileToFunctions -> compile -> baseCompile
核心是 baseCompile 生成 render 方法,其中涉及到 解析template为AST 抽象语法树,最大静态子树的提取
有兴趣可自行分析 ./parser/index.js 代码,此处不展开
技术栈学习资料
- MVVM框架: Vue 2.0
- 源码:es6
- 代码风格检查:eslint
- 构建工具:webpack2.0
- 前端路由:vue-router
- 状态管理:vuex
- 服务端通讯:vue-resource
- vue UI组件库:vux
- 基于vue2.0实现的多页面项目雏形:sgoddon-vux





